Hip preservation treatments have seen significant advancements in recent years, offering patients more options for managing hip-related conditions while delaying or avoiding the need for total hip replacement. As medical technology and surgical techniques continue to evolve, the landscape of hip preservation is changing, providing new hope for those suffering from hip dysplasia, labral tears, femoroacetabular impingement (FAI), and other hip disorders. This article explores the latest innovations in hip preservation treatments and how they are transforming patient care.
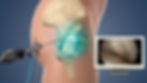
1. Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques
One of the most significant innovations in hip preservation is the development of minimally invasive surgical techniques. Procedures such as hip arthroscopy have become increasingly popular due to their ability to treat various hip conditions with smaller incisions, reduced pain, and quicker recovery times. Hip arthroscopy allows surgeons to repair labral tears, reshape bone to correct impingement, and remove loose bodies from the joint, all while minimizing trauma to surrounding tissues.
Key Benefits:
Shorter hospital stays
Faster rehabilitation
Less postoperative pain
Reduced scarring
2. 3D Imaging and Preoperative Planning
Advances in imaging technology, particularly 3D imaging, have revolutionized the way surgeons plan and execute hip preservation surgeries. 3D models of the hip joint allow for more precise preoperative planning, enabling surgeons to better understand the patient’s unique anatomy and tailor the surgery to their specific needs. This technology is particularly beneficial in complex cases of hip dysplasia, where accurate reorientation of the hip socket is crucial.
Key Benefits:
Enhanced surgical precision
Reduced risk of complications
Improved patient outcomes
3. Biologic Treatments and Regenerative Medicine
Biologic treatments, including the use of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and stem cell therapy, are emerging as promising options in hip preservation. These treatments aim to enhance the body’s natural healing processes by promoting tissue regeneration and reducing inflammation. PRP involves injecting a concentrated form of the patient’s own platelets into the affected area, while stem cell therapy uses cells that can differentiate into various tissue types to repair damaged cartilage or tendons.
Key Benefits:
Minimally invasive with fewer side effects
Potential to delay the progression of joint degeneration
Can be used in conjunction with surgical procedures to enhance healing
4. Computer-Assisted and Robotic Surgery
Computer-assisted and robotic surgery are at the forefront of innovation in hip preservation. These technologies provide surgeons with enhanced visualization and precision, allowing for more accurate placement of implants and more consistent surgical outcomes. Robotic systems can assist in performing complex procedures such as PAO with greater accuracy, potentially reducing the risk of human error.
Key Benefits:
Increased surgical precision
Consistent, reproducible outcomes
Enhanced safety and reduced complications
5. Enhanced Postoperative Rehabilitation Protocols
Innovations in postoperative care are just as important as surgical advancements. New rehabilitation protocols that incorporate the latest in physical therapy techniques, wearable technology, and patient education are helping patients recover more quickly and effectively after hip preservation surgery. Customized rehabilitation plans that focus on gradual return to activity, strength training, and mobility exercises are critical for optimizing long-term outcomes.
Key Benefits:
Accelerated recovery timelines
Improved long-term mobility and function
Reduced risk of postoperative complications
6. Emerging Non-Surgical Interventions
While surgery remains a key component of hip preservation, non-surgical interventions are also evolving. New treatments, such as advanced physical therapy techniques, joint injections with novel biologic agents, and lifestyle modifications, are helping patients manage symptoms and improve hip function without the need for invasive procedures. These innovations are particularly beneficial for patients who are not yet candidates for surgery or who wish to delay surgical intervention.
Key Benefits:
Non-invasive with minimal recovery time
Effective in managing early-stage hip conditions
Can be used in conjunction with other treatments for comprehensive care
Conclusion
The field of hip preservation is rapidly advancing, offering patients more effective and less invasive treatment options than ever before. From minimally invasive surgical techniques to biologic treatments, these innovations are transforming the way hip conditions are managed, providing hope for better outcomes and improved quality of life. If you or a loved one is dealing with a hip condition, staying informed about these advancements can help you make the best decisions for your health and well-being. Always consult with a specialized orthopedic surgeon to explore the most suitable treatment options for your specific condition.
.png)






